Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that the sodium-potassium-chloride co-transporter 1 (NKCC1) and potassium-chloride co-transporter 2 (KCC2) have a role in the modulation of pain transmission at the spinal level through chloride regulation in the pain pathway and by effecting neuronal excitability and pain sensitization. Dr. Yanbing He Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, China and his team found that intrathecal bumetanide could increase NKCC1 expression and decrease KCC2 expression in spinal cord neurons of rats with incisional pain. The authors presumed that intrathecal bumetanide has analgesic effects on incisional pain through inhibition of NKCC1. This paper was published in Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 10, 2014).
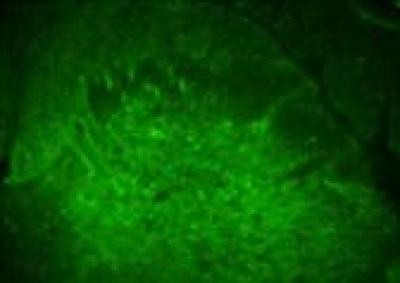
Immunofluorescent staining reveals that potassium-chloride co-transporter 2 expression decreases in the deep laminae of ipsilateral dorsal horn of L4-5 spinal cor after incision.
(Photo Credit: Neural Regeneration Research)
Source: Neural Regeneration Research