Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and neuregulin 1 (NRG1) are important genes and signaling pathways that are altered in schizophrenia. To date, no studies have reported magnetic resonance spectroscopy in a rat model of schi-zophrenia induced by early growth response protein 3 gene (Egr3) transfection. Prof. Guolin Ma and colleagues from China-Japan Friendship Hospital, China used multivoxel proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy to study neuronal metabolite content in rats transfected with the Egr3 gene as a putative model of schizophrenia. 3.0 T proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of in vivo brain tissues showed metabolic abnormalities in hippocampal and thalamic neurons of growth response protein 3 transfected rats. These findings, published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 8, No. 26, 2013), provide imaging evidence that may be useful in the early diagnosis and pathogenesis of schizophrenia.
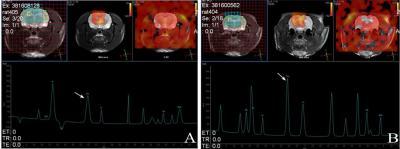
This is a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the hippocampus and thalamus of early growth response protein 3 gene-transfected rats.Choline (Cho; arrow represents Cho peak) content was increased in the left hippocampus of schizophrenic rats (A) compared with bilateral hippocampi of control group (B).
(Photo Credit: Neural Regeneration Research)
Source: Neural Regeneration Research