CLARITY provided this 3D view showing a thick slice of a mouse brain's memory hub, or hippocampus. It reveals a few different types of cells: Projecting neurons (green), connecting interneurons (red), and layers of support cells, or glia (blue). Conventional 2D methods require that brain tissue be thinly sliced, sacrificing the ability to analyze such intact components in relation to each other. CLARITY permits such typing of molecular and cellular components to be performed repeatedly in the same brain.
(Photo Credit: Karl Deisseroth, M.D., Ph.D., Stanford University)
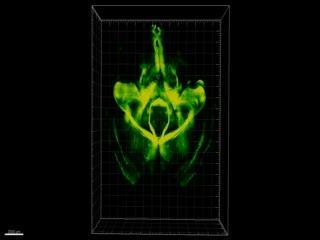
CLARITY makes possible this 3D tour of an entire, intact mouse brain. It was imaged using a fluorescence technique that previously could only be performed with thinly-sliced brain tissue, making it difficult to relate micro-level findings to macro-level information about wiring and circuitry.
(Photo Credit: Source: Karl Deisseroth, M.D., Ph.D., Stanford University)