Endoplasmic reticulum stress is closely involved in the early stage of diabetic retinopathy. According a study published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 8, No. 33, 2013), endoplasmic reticulum stress played an important role in the hyperglycemia-induced death of ganglion cells and impairment of retinal microvessels. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid treatment effectively inhibited the activation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway, and provided effective protection against diabetic retinopathy. The C/ERB homologous protein was shown to co-localize with glial fibrillary acidic protein-positive glial cells in the retina of diabetic rats, and subsequently provided evidence for the activation of glial cells in diabetic retinopathy.
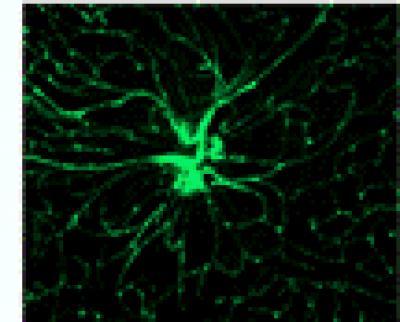
After onset of diabetes, the retina from diabetic rats exhibited focal dilation of retinal capillaries, with vessels tortuosity and sac-like bulges in the vessel wall (fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran angiograph, light microscopy).
(Photo Credit: Neural Regeneration Research)
Source: Neural Regeneration Research