WASHINGTON, Sept. 13—Researchers at Vanderbilt University have developed a new technique that uses a single UV laser pulse to zap away biological tissue at multiple points simultaneously, a method that could help scientists study the mechanical forces at work as organisms grow and change shape.
UV lasers are a commonly-used tool for cutting into tissue, but the lasers usually make incisions by vaporizing one point at a time in a series of steps. If the initial laser pulse cuts into cells under tension, the tissue could spring back from the incision. This makes precise tasks, such as cutting around a single cell, difficult. The Vanderbilt team found a way around this problem by using a computer-controlled hologram to shape the phase profile of the UV pulse –basically applying a patterned delay onto different parts of the beam. When the pulse then passed through a lens, the altered phase profile yielded an interference pattern with bright spots at any user-desired pattern of points. Using this method, which can vaporize up to 30 points simultaneously, the researchers successfully isolated a single cell on a developing fruit fly embryo and then observed how the cell relaxed into a shape dictated solely by internal forces.
The technique, described in the September issue of the Optical Society's (OSA) open-access journal Biomedical Optics Express, could be applied to other model organisms, such as frogs or zebra fish, to help answer
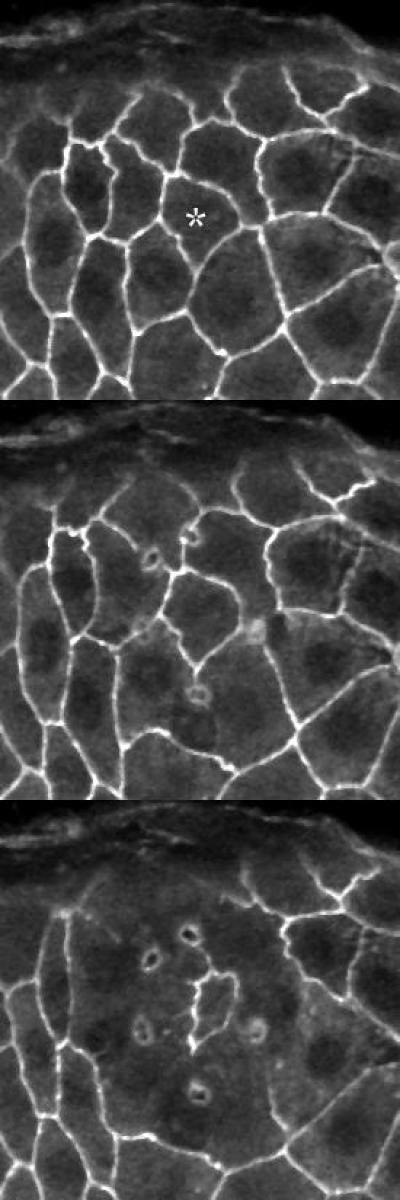
Time-lapse microscopy of a fruit fly epithelium in which a single cell is isolated from the remainder of the cell sheet using a single holographically-shaped laser pulse. The cell-to-be-isolated is marked with an asterisk in the first frame. Subsequent frames are at 6 s and 70 s after ablation.
(Photo Credit: Aroshan K. Jayasinghe)
outstanding questions in developmental biology. This knowledge may in turn guide bioengineers searching for ways to grow designer tissue.

Time-lapse microscopy of a fruit fly epithelium in which a single cell is isolated from the remainder of the cell sheet using a single holographically-shaped laser pulse. Progression in time is color-coded from blue to red to white.
(Photo Credit: Aroshan K. Jayasinghe.)
Source: Optical Society of America