Oxidative stress is closely associated with secondary cell death in many disorders of the central nervous system including stroke, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease. Among many aberrant oxidative stress-associated proteins, DJ-1 has been associated with the oxidative stress cell death cascade primarily in Parkinson's disease. Although principally expressed in the cytoplasm and nucleus, DJ-1 can be secreted into the serum under pathological condition. Recently, a close pathological association between DJ-1 and oxidative stress in stroke has been implicated. To this end, Prof. Cesar V. Borlongan, who comes from University of South Florida, USA and his team and others have demonstrated the important role of mitochondria in neuroprotection for stroke by demonstrating that the translocation of DJ-1 in the mitochondria could potentially mitigate mitochondrial injury. Here, we discuss our recent findings testing the hypothesis that DJ-1 not only functions as a form of intracellular protection from oxidative stress, but that it also utilizes paracrine and/or autocrine cues in order to accomplish extracellular signaling between neighboring neuronal cells, resulting in neuroprotection. This article highlights recent evidence supporting the status of DJ-1 as key anti-oxidative stress therapeutic target for stroke. The relevant study has been published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 15, 2014).
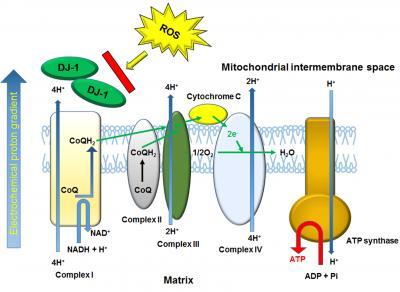
This image represents a aummarized DJ-1 function for protecting mitochondrial function.
(Photo Credit: Neural Regeneration Research)
Source: Neural Regeneration Research