Dr. Yuhong Zhao and co-workers from Sun Yat-sen University in China explored the projection of nestin+ neurons to the olfactory bulb and the time course of nestin+ neurons in the medial septum-diagonal band of Broca in adult rats during injury recovery after olfactory nerve transection. These researchers observed that all nestin+ neurons were double-labeled with ChAT in the medial septum-diagonal band of Broca. Approximately 53.6% of nestin+ neurons were projected to the olfactory bulb and co-labeled with fast blue. A large number of nestin+ neurons were not present in each region of the medial septum-diagonal band of Broca. Nestin+ neurons in the medial septum and vertical limb of the diagonal band of Broca showed obvious compensatory function. The number of nestin+ neurons decreased to a minimum later than nestin–/ChAT+ neurons in the medial septum-diagonal band of Broca. Their results suggest that nestin+ cholinergic neurons may have a closer connection to olfactory bulb neurons. Nestin+ cholinergic neurons may have a stronger tolerance to injury than Nestin–/ChAT+ neurons. The relevant study has been published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 3, 2014).
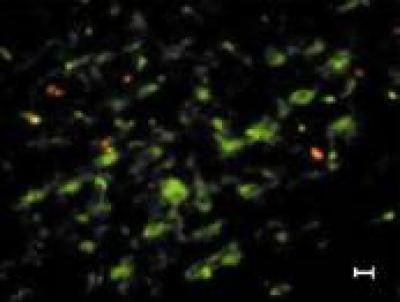
To confirm if the increased nestin+ neurons in the medial septum-diagonal band of Broca came from the differentiation of immature cells, the rats were injected with BrdU after olfactory nerve transection. Using double fuorescent immunocytochemistry for nestin and BrdU, nestin+ neurons in the olfactory nerve transection group showed clear nestin immunoreactivity in cell bodies. Clear BrdU immunoreactivity was visible in nuclei labeled by red fuorescence in the medial septum-diagonal band of Broca (Figure 4B). However, nestin+/BrdU+ neurons were not observed in cells of sagittal or coronal slices.
(Photo Credit: Neural Regeneration Research)
Source: Neural Regeneration Research