Electroacupuncture has traditionally been used to treat pain, but its effect on pain following brachial plexus injury is still unknown. In a recent study reported on the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 14, 2014), rat models of an avulsion injury to the left brachial plexus root (associated with upper-limb chronic neuropathic pain) were given electroacupuncture stimulation at bilateral Quchi (LI11), Hegu (LI04), Zusanli (ST36) and Yanglingquan (GB34). After electroacupuncture therapy, chronic neuropathic pain in the rats' upper limbs was significantly attenuated. Immunofuorescence staining showed that the expression of β-endorphins in the arcuate nucleus was significantly increased after therapy. Thus, Shenyu Zhang and co-workers from Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, China, indicate that electroacupuncture can attenuate neuropathic pain after brachial plexus injury through upregulating β-endorphin expression.
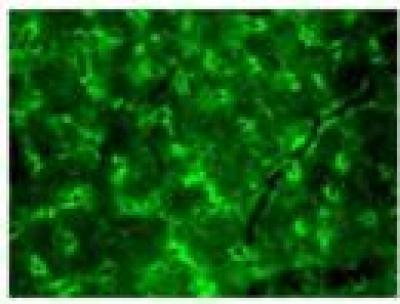
The number of β-endorphin positive cells was significantly increased after 28 days of electroacupuncture therapy (immunofluorescence staining).
(Photo Credit: Neural Regeneration Research)
Source: Neural Regeneration Research