WASHINGTON, D.C. Nov. 1, 2013 -- Most people know about ultrasound through its role in prenatal imaging: those grainy, grey outlines of junior constructed from reflected sound waves. A new technology called an "acoustic diode," envisioned by researchers in China's Nanjing University, may dramatically improve future ultrasound images by changing the way sound waves are transmitted.
In the journal Applied Physics Letters, which is produced by AIP Publishing, the scientists describe the theoretical framework for an acoustic diode -- a device that achieves a one-way transmission of sound waves much the same as an electrical diode controls the one-way transmission of electrical impulses.
The one-way flow of sound would provide brighter and clearer ultrasound images by eliminating acoustic disturbances caused by sound waves going in two directions at the same time and interfering with each other, explained researcher Jian-chun Cheng.
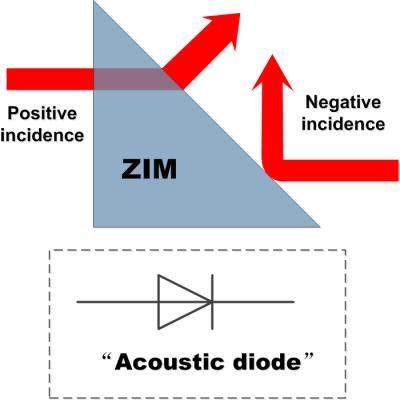
This is a schematic illustration of "acoustic diode" made of a zero refractive-index medium (ZIM) prism, which only allows the acoustic waves comes from the left ("positive incidence") to pass but blocks the waves from right ("negative incidence").
(Photo Credit: Urbana/ B. Liang)
"The propagation direction of the output wave would be controlled freely and precisely," Cheng said. "These features are crucial for the medical ultrasound applications of the resulting devices."
How the Acoustic Diode Would Work
Sound waves easily flow in two directions. Yet in nature, total reflection of sound in one direction is known to occur at the air-water interface. This gave investigators the idea that an acoustical diode could be constructed by transmitting acoustic waves using an asymmetric prism to create total unidirectional reflection.
The team developed its theoretical model based on a material not found in nature called a near-Zero Index Metamaterial (ZIM) and a prism to create high transmission efficacy acoustic waves that strike a reflective boundary from two opposite sides.
In theory, explained Dr. Cheng, "This would produce a unique tunneling effect and an unprecedented property that the output waveform is kept consistent with those of the waves traveling toward a boundary. "
Source: American Institute of Physics