Activated microglia-mediated inflammation promotes neuronal damage under cerebral hypoxic-ischemic conditions, so it is likely that inhibiting hypoxia-induced activation of microglia will alleviate neuronal damage. To test this hypothesis, Dr. Lining Ke and co-workers from Southern Medical University and Fujian Medical University in China co-cultured ginsenoside Rb1, an active component of ginseng, and cortical neurons. Their findings indicate that ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates damage to cerebral cortex neurons by downregulation of nitric oxide, superoxide, and tumor necrosis factor-α expression in hypoxia-activated microglia. This study, which has been published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 3, 2014), suggest that ginsenoside Rb1 is a promising candidate for clinical use in the prevention of neuronal degeneration following cerebral ischemia.
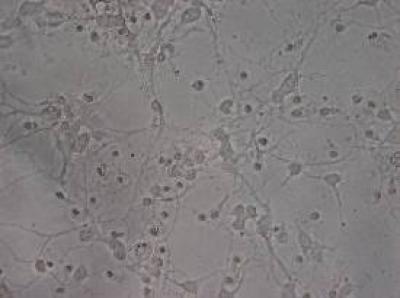
This shows pre-hypoxic neurons co-cultured in medium from microglia exposed to hypoxia: The number of cultured cells was significantly lower than in the control group, the residual cells appearing deformed, with fractured or absent processes, and a large amount of debris present from dead cells.
(Photo Credit: Neural Regeneration Research)
Source: Neural Regeneration Research