Aberrant Wnt signaling is possibly related to the pathological changes in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Axin and β-catenin protein is closely related to Wnt signaling. Zhou Hua and his team, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, China confirmed that moxibustion or electroacupuncture, or both, at Baihui (GV20) and Shenshu (BL23) acupoints decreased axin protein expression, increased β-catenin protein expression, and alleviated neuronal cytoplasmic edema. These findings suggest that the mechanism underlying the neuroprotective effect of acupuncture in AD is associated with axin and β-catenin protein expression in the Wnt signal transduction pathway. Related results were published in Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 9, 2014).
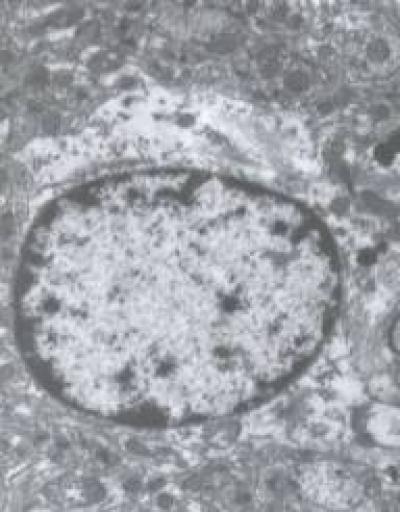
The edema of hippocampal neurons in Alzheimer's disease rats was significantly alleviated after electroacupuncture and moxibustion pretreatment (transmission electron microscope, × 8 000).
(Photo Credit: Neural Regeneration Research)
Source: Neural Regeneration Research