A 9,000 year-old case of human decapitation has been found in the rock shelter of Lapa do Santo in Brazil, according to a study published September 23, 2015 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by André Strauss from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, Germany and colleagues.
An archaeological site called Lapa do Santo, located in east-central Brazil, contains evidence of human occupation dating back to ~12,000 years ago. In 2007, researchers found fragments of a buried body, Burial 26, including a cranium, jaw, the first six cervical vertebrae, and two severed hands at the site. They dated the remains back to ~9,000 years ago using accelerator mass spectrometry. The researchers found amputated hands laid over the face of the skull arranged opposite each other and observed v-shaped cut marks on the jaw and sixth cervical vertebra.
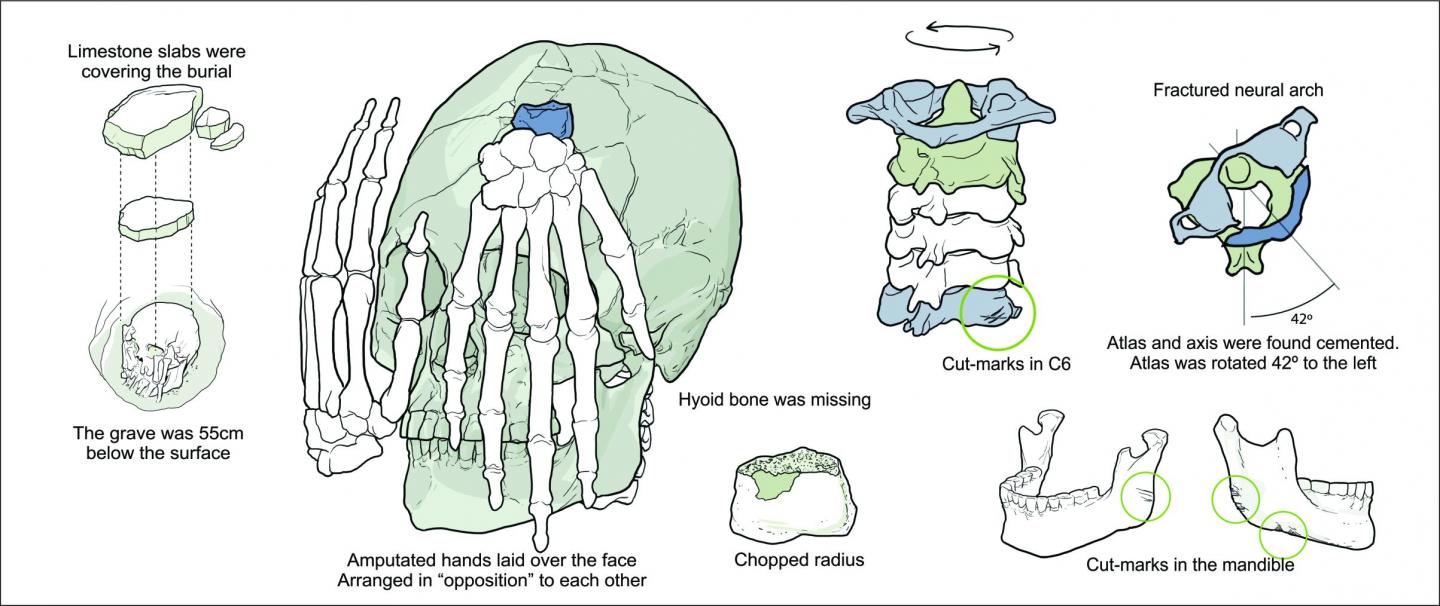
A schematic representation of Burial 26 from Lapa do Santo. Credit: Drawing by Gil Tokyo.
Based on strontium analysis comparing Burial 26's isotopic signature to other specimens from Lapa do Santo, the researchers suggest Burial 26 was likely a local member of the group. Additionally, the presentation of the remains, lead the authors to think that this was likely a ritualized decapitation instead of trophy-taking. If this is the case, these remains may demonstrate sophisticated mortuary rituals among hunter-gatherers in the Americas during this time period. The authors think this may be the oldest case of decapitation found in the New Word, leading to a re-evaluation of the previous interpretations of this practice, particularly with regards to its origins and geographic dispersion.